The modern bioprocessing Technology is the subdiscipline within biotechnology which functions as a translator in between the discoveries of life science into practical products, processes, or systems that can be served the needs of society. The biotechnologist having an obvious knowledge of Bioprocess has many missions. Although the most visible today is the production of biopharmaceuticals, bioprocess technology also has a major role in the existing multi-billion-dollar fermentation industries responsible for the production of ethanol, amino acids, and other organic acids, antibiotics, and other specialty products.Fig1. represent the growing scope area of bioprocess technology.
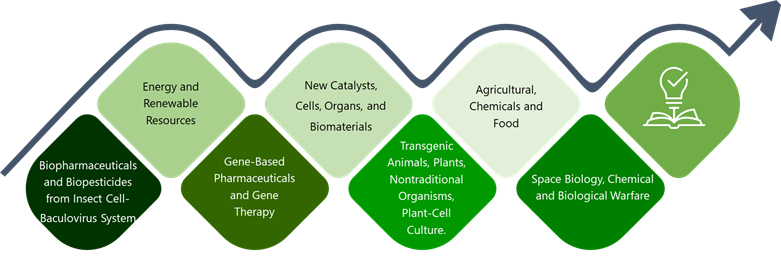
Figure 1. The diverse growing spectrum of bioprocess technology.
Biopharmaceutical biologic such as insulin, tissue plasminogen, activator, and erythropoietin are the dominant products in current bioprocess technology products and predominantly controls commercial activities related to biotechnology. Innovations in bioprocess engineering to manufacturing these products can be of great consequences. Those will help in improving product recovery, product purity, process safety and reduce manufacturing and quality-control costs. Process innovation is also one of the needs which can intensify as patent protection for the product expires and increase global competition for international markets and regulatory procedures.
There will be significant growth in the usage of health care products emerging from biotechnology all over the world in comparison to the current scenario (examples include recombinant hemoglobin, recombinant albumin, and conjugate vaccines). There will be demand for second-generation products as well; large scale manufacturing facilities that handle biological systems and bioprocess technology will be in the spotlight and essential for successful commercialization for products.
The current Covid-19 crisis changes the dynamics of bioprocessing. Specifically, there are two different spectra of impact on the bio-process market, one is a short term, another is long term.
Essentially all the bioprocessing related industries are mostly unaffected and continuing their operations as expected however there are short-term impacts in some areas of bioprocessing sector are facing operational challenges for the lower number of available resources during a pandemic.
As expected, many companies, including developers and suppliers of hardware and services, are increasing their pandemic-related R&D and manufacturing. Suppliers are expecting and planning for increased business as companies and governments start to rapidly develop, test, and deploy pandemic-related vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics. There has been a spike in demand for stockpiling the supplies but that’s for the short-term. As per the economic stress is concerned healthcare segments are less sensitive.
The general expectation is that there will be relatively minimal adverse near/short-term economic impact and its aftermath on the bio-processing sector as a result of the pandemic. Most companies are sticking to their long-term capital-intensive expansions and mergers/acquisitions.
Several fundamental changes are going to take place in the ‘Post-COVID’ era which will evolve as a result of the pandemic and those changes will last for the long term.
Many of these, such as-
- the increase in the number of global facilities,
- more pandemic-related R&D and manufacturing,
- quick supplies and services,
- more modular facilities,
- single-use systems (SUS) process lines and facilities,
- faster R&D and speed-to-market,
- more collaboration,
- more investment,
- more automation will be prioritized.
The novel Covid-19 appears to be a catalyst for the acceleration of existing and emerging trends in the industry.
Bioprocess technology can play a major role to produce new smaller molecules and special bioproducts by application of bio-knowledge and technology. A major challenge is to get value-added products on a large scale by applying bioprocessing. Those are integrated processes that use agricultural and forestry-based materials and other renewable resources. Byproducts of food production (animal health-care, biological plant-growth promoters and pesticides, nutritional supplements, and food additives) have large-tonnage product opportunities and those can be tapped in the coming decade, provided that suitable manufacturing facilities are designed and built. Currently, these facilities do not exist and the major challenge for bioprocessing is to make those facilities created and available. Proper infrastructure for practical implementation needs to be developed along with the process knowledge enhancement program because, in the coming decade, the processing of renewable resources will be one of the topmost priorities throughout the nation. Bioprocessing in space presents unique opportunities, particularly in bio-regenerative life support and as a research platform for the study of unfamiliar types of manufacturing processes.
As per the recent survey, bioprocess companies have displayed robust nature to deal with the pandemic and tried to keep the business uninterrupted. The current crisis has given enough fuel to bioprocess industries to prepare for future pandemics. There will be some long-term adjustments to handle any crisis; new strategies are going to be in place to moderate future supply shortages, collaborative relationship with research & development team and the suppliers need to be developed, rapid and flexible implementation and modular production process to speed up the supply to the market. Manufacturing industries will be affected which these changes; may not be now but after the crisis resolves.



