In Memory of: Prof. Ananda Mohan Chakraborty (1938-2020)
Dr. Saptarshi Chatterjee, Dr. Sanmitra Ghosh, Dr. Neloy Kumar Chakroborty, Dr. Arijit Bhattacharya, Dr. Arindam Mitra
Introduction: ‘Life’fascinates everyone while many are interested in the ‘Study of Life’. Thus, Biology or Life Science, per se, remains as a preferred subject for many students at the school level. The study of exquisite functioning of cellular machinery to the study of complex organ systems create a deep inquisitiveness of knowing the life forms; be it plants, animals or human. Gradually, the students aspire to take up such studies as their career path. However, a major section of the students gets confined to the conventional options of either becoming a doctor or studying botany, zoology or physiology in a degree course at the graduation level. This article speaks about the domain of microbiology, a field with immense scope, job opportunities and a rewarding career beyond the conventional options.
Before we move on to the career aspects of microbiology, let us read a biography and try to identify the personality.
“The microbiologist was born in Sainthia, Birbhum District of West Bengal, studied at Ramakrishna Mission, Vidyamandir and St. Xavier’s College, Kolkata. He received his Ph.D. from the University of Calcutta. His famous contribution was the development of an oil-eating bacterium, Pseudomonas putida; a genetically modified organism that brought laurel to his name. This internationally recognised microbiologist has founded a company (CDG Therapeutics) and was serving as a Distinguished University Professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Illinois, USA. His name features in every textbookfor his landmark contribution in applications of microbiology.”
He was none other than Prof. Anandamohan Chakraborty.
The current pandemic of COVID-19 has challenged the humanity, especially the scientific community, globally. However, people who took up the challenge and working relentlessly to overcome the situation are health care workers, scientists and researchers. Among them, the role of microbiologists (predominantly the virologists) demands special attention. So, let us first understand Microbiology as a domain of study.
Microbiology as a Subject: Microbiology is the study of organisms that cannot be seen usually without unaided eyes. The basic components of studying microbiology are the microorganisms, which are microscopic in nature viz. bacteria, virus, algae, fungus, protozoa, prions and viroids. A program in the undergraduate or postgraduate level in microbiology has a blend of basic, applied and advanced aspects to provide an in-depth knowledge of the domain and develop skill sets suited for industries. While the basic subjects like chemistry, biochemistry together with the options of zoology, botany etc. create the fundamentals for studying advanced subjects like molecular biology, biotechnology etc., microbiology is a unique mother subject that offers the opportunity to study specialized applications through the courses, like medical microbiology, agricultural microbiology, industrial microbiology, food and dairy microbiology etc. (Figure 1). Thus most of the colleges and universities are following the model curriculum of ‘Choice Based Credit System (CBCS)’ as prescribed by the University Grants Commission, India, which is a perfect blend of basic and applied microbiology, to give an excellent opportunity to the graduates in excelling their desired career. However, some colleges and universities have further modified their curriculums to suite the demands of various industries.

Figure 1: Various subjects taught in the Microbiology curriculum.
Looking Beyond the Medical Education: Medical entrance examination is one of the toughest selection processes in India and statistically in 2020, approximately 16 lakh applicants would contest for the 70,000 limited medical seats available across the country. Understandably, the major fraction of students cannot secure a seat either in the MBBS or BDS examinations, though surely a healthy proportion of these candidates should achieve bright careers. Therefore, we need to realise that a single examination system neither can be a full-proof yard-stick to measure the ability of the aspirants nor it should decide their fates. Hence rejected applicants, with the common mental state of ‘compromising on aspiration’ need counselling for proper guidance and motivation, which can help them to select the correct alternative subject and become successful professionals in their chosen field. Their aspiration and dreams can take the shape of dedicated researchers working in microbiology and impact millions of lives worldwide by developing novel vaccines or antimicrobials. Therefore, failure to secure a seat in the MBBS or BDS examination may present students to look beyond through the lens of Microbiology and explore its diverse career paths and job opportunities.
Career Path of Microbiology: Microbiology offers a lucrative career path and scope for employability after completion of the graduation (B. Sc.) level. However, the scope increases progressively after successive completion of post-graduation (M.Sc.), Ph.D. and postdoctoral training. Figure 2 illustrates the career paths and options for students in Microbiology.

Lateral and Vertical Mobility: Studying microbiology in the graduation level opens up a lot of scope for moving towards higher education both in microbiology and in allied disciplines, such as Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, and even others like Management (MBA) etc. Therefore, having a basic degree as B. Sc. in microbiology can benefit immensely in moving up the ladder and migrating to other branches of life science or other fields of studies.
Job Prospects in Microbiology: Among the domains of biological sciences, microbiology stands apart and well ahead in providing job opportunities to the students at various levels (Figure 3). This is because of the fundamental nature of the subject, with blended advanced curriculum containing knowledge from the specialized and applied domains. Unlike Biotechnology, which being a non-mother subject is an amalgamation of knowledge from different mother subjects, microbiology provides the specialized knowledge and skill sets required by the employers across the global. An important example is that microbiologists comprise an important part of the quality management system (QMS) of various industries to fulfil the mandatory and regulatory compliance.
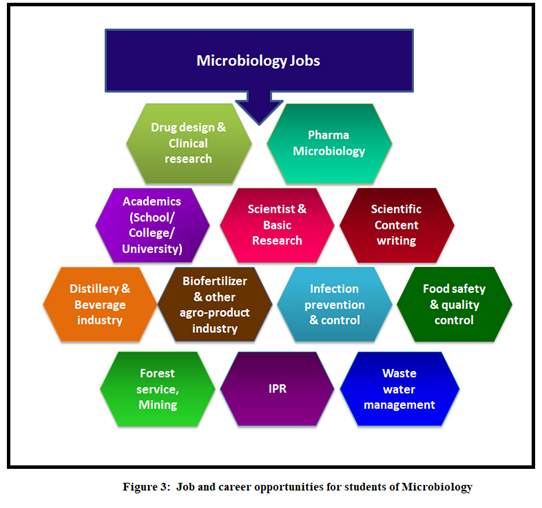
Job descriptions of Microbiologists in selected domains are discussed below:
- Quality Control (QC) in Food & Pharmaceutical Industries: Monitoring of raw material or final product quality is an essential aspect of the quality management system. Every food and pharmaceutical industry mandatorily need to recruit microbiologist as the QC officer as per regulatory compliance to look into the microbial aspects of QC to produce products safe for consumption and use.
- Food Safety: ‘Safe food’ is a food devoid of ‘microbial contamination’ so that it does not contain any toxin or pathogens able to cause harm after consumption. Therefore, not only the food industries but also the health regulators, municipalities, local civic bodies recruit microbiologists as food safety officers to judge the quality of food being prepared and sold. It is a part of the public health policy of every government that generates a lot of employability specifically to microbiology students at the graduation or post-graduation level.
- Infection Prevention & Control (IPC): Every hospital and clinical setup requires trained microbiologists as IPC Officer to look into the aspects of preventing infection. They work with the clinicians to efficient disease management.
- Clinical Research Professionals: With emergence of novel pathogens and diseases, clinical complications, drug resistance, there is always a scope for the development of novel formulations as drug. After the successful research outcome in a laboratory, it has to go through stringent procedure of Clinical Trial involving toxicity testing, dosage determination, experiment in animal model and human. Microbiologists have option to work as clinical trial coordinators and pharmacovigilance officers in various clinical trials conducted worldwide.
- Quarantine & Inspection: Foods, animals and even human can act as source or reservoir of causative agents of several diseases. Transport of such from one place to another should be based on norms and free from disease. Therefore, governments employ quarantine officers, who are trained microbiologists capable of carrying out inspection of items, analyse the health, suggest testing and recommend actions of quarantine.
- Researchers (Basic): Joining research program after post-graduation is a lucrative option that has significant scope of earning as well as obtaining higher degree, contributing to human welfare through research. Positions like Junior Research Fellow (JRF) and Senior Research Fellow (SRF) offered by research institutes and universities based on research funding from Department of Science & Technology (DST), Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Science & Engineering Research Board (SERB), University Grants Commission (UGC) etc.
- Laboratory Technicians: Modern science depends on the sophisticated instrumentation and thus requires specific skill-sets for conducting experiments and handling of such equipment like PCR, HPLC, GC, AAS, FACS, RT-PCR, Confocal Microscopy, Electron Microscopy (TEM/SEM) etc. Microbiologists, as trained professional are suitable to use such instruments and work on BSL-I to BSL-IV lab maintaining guidelines and taking protective measures. Several diagnostic labs conduct basic microbiology and molecular testing and recruit microbiologists.
- Scientists: To know the unknown and creation of new has always fascinated the best minds in science. Therefore, the option of being a scientist and carry out independent research in an industry or govt. research institute is always opens to microbiologists. They are free to select any particular domain of biological sciences in carrying out cutting-edge research utilizing state-of-art laboratories at various organizations. Collaboration between multiple institutes provides them the scope to serve mankind in the form of finding solution to the most relevant problem of the day.
- Production involving Fermentation: Distilleries and beverage industries use microorganisms for the process involving fermentation to obtain products like alcoholic beverage, enzymes and others. These productions require steps like strain improvement, culture maintenance, inoculum preparation, product recovery etc. generating huge scope of employment for microbiologists.
- Agro-product development: Because of the adverse effect of chemical fertilizers on soil, food products and environment, the focus of today’s agriculture is on bio-fertilizers. Most of them are live microorganisms packed for field applications. Therefore, productions of these bacterial or fungal strains require trained microbiologists, thereby enhancing job opportunities in the agricultural sector.
- Wastewater Management: Several industries and municipal authorities require wastewater treatment to be done before releasing it to the environmental bodies. Similarly, effluent treatment in modern days is carried out utilizing the potential of microorganisms to detoxify hazardous chemicals as well as to breakdown materials into simpler forms. Microbiologists are recruited to maintain the process as well as microbial monitoring.
- Faculty Position: Teaching is a preferred profession due to its noble nature and ability to contribute towards societal development. Microbiology offers prominent opportunity to take up employment opportunity at School, college and university level. While PG degree with B.Ed. is essential for the position of Assistant Teacher, a Ph.D. followed by post-doctoral experience is desired for positions of Assistant Professor in colleges and universities.
- Scientific Content Writing: With the advent of digital era, development of content became crucial and opened up scope for employment. Several organizations employ personnel having sound technical knowledge on domain as content writers. Facility of work-from-home and part-time involvement has attracted a lot of microbiology students to take it up as career option.
- IPR: Securing the intellectual property through IPR laws of the country is considered as an important parameter in determining scientific growth of a nation. IPR despite of being a domain of law requires expert from every discipline to understand technical aspects related to innovation in biological sciences. IPR professionals are recruited in private and government sector as professionals. It is increasingly being popular among present days student.
- Business Development: Modern business development and marketing demands the understanding of commodity in technical terms and ability to troubleshoot in real time rather than conventional sales strategies. Therefore, huge number of scientific products from medicine to instruments has a wide market to be captured by people knowledgeable in the domain along with appropriate skills. This is another broad scope of employment generation among microbiology students.
- Entrepreneurs: The present generation has raised their level of thought in establishing their own enterprise as start-ups, despite of job offers. Their intention to make self-reliant India is well supported by governments, banking sector and others. Own start-up employing technology-based business has great potential in the days ahead and ignited the best minds to think beyond jobs in their domain. Several examples exist from agricultural products to pharmacy where microbiologists are successful in their endeavour.
- Government Services: Apart from the teaching, research and technical services of the government, microbiologists can also aspire to take up civil service examinations of state and central government. Moreover, the option of joining as school teacher also remains open once, students aspire so.
Future Scope:
The occurrence of back-to-back viral epidemics and the current global pandemic has at least made the scenario clear to the world that we need numerous numbers of research scientists in the field of animal and veterinary virology. This urgent requirement can be best fulfilled by training the potential candidates with an academic background in Microbiology.


