Multinational companies are spending fortunes to protect and secure their systems, sensitive data, networks, and privacies from cybercriminals. After the pandemic, with proliferation of internet use and technology use, these cyber attacks become more refined and inventive, forcing the organizations to depend on the proficiency of the cybersecurity professionals.
As per CyberSeek report, around half million cybersecurity professionals are required to fulfill the gap. It is best time to become a cybersecurity professional because of this rising demand and small talent pool. There are some lucrative job opportunities available for those persons with relative technology focused skill. Even if someone does not have prior experience in cyber security domain, getting a job in this domain is possible. With the increase of frequency in cyber-attacks, almost all the organizations are recruiting to defend against these kinds of threats. There are various career paths available for the students who interested in making the career out of cyber security professional.
Like machine learning and data science, Cyber security career paths are also multidirectional as well as non-linear. Once someone enters the domain, his/her career can go in any direction. Along with that there are also feeder roles like risk analyst, software engineer, network administrator which can be used as a beginner level cyber security professional.
When anyone thinks of cybersecurity jobs, generally the first think comes into our mind is someone trying penetrate the networks or systems which is basically penetration testing or ethical hacking. But this notion is nothing but the tip of an iceberg. Cybersecurity is bigger than that. It contains various sub categories and specialization and all of these can be broadly categories in to two parts i.e., Infrastructure management and Security and Risk Management.
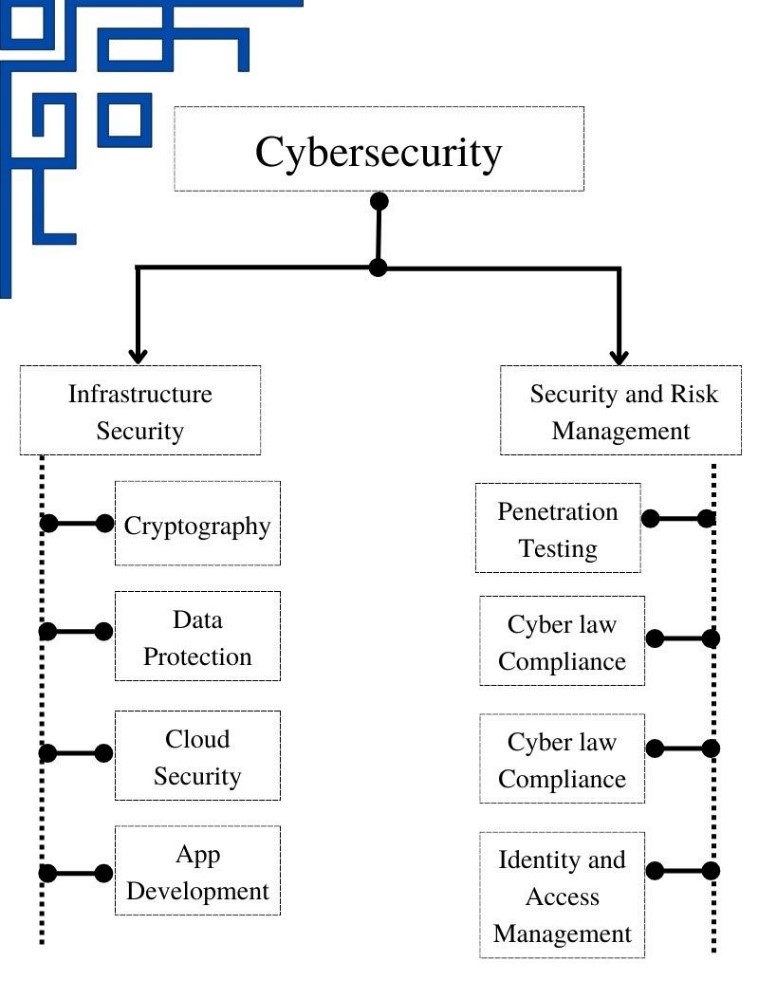
Infrastructure Security
Networking infrastructures are extremely important to multinational business organizations. Cybercriminals can readily access and exploit sensitive resources and information if they are not properly protected. Cybersecurity specialists must design, firewalls, virtual private networks, application security, and many more to mitigate security and data breaches.
Common job roles for the protection of infrastructure are given below:
- Security Operations Center (SOC) analyst
- Security infrastructure engineer
- Cybersecurity engineer
- Security architect
- Cloud security engineer
Security and Risk Management
Security and risk management actually constitute ensuring that businesses follow security regulations and procedures, as well as undertaking risk assessment to determine security flaws in tangible infrastructure, business applications, and data. Penetration testing and compliance are useful roles in this niche. In fact, compliance has become so critical that some industries even have entire squad devoted entirely to data governance and privacy protection.
Common job roles for Security and Risk Management are given below:
- Penetration tester
- Data privacy and security analyst
- Security compliance analyst
- Information security analyst
- Cyber Security Incident Response Analyst
Skill requirement for cybersecurity
Even though cybersecurity jobs may appear to be extremely specialized and computational-intensive, these skilled persons have the know-how of various different but interrelated domains. It is expected that these professionals have some specific skill sets in both hard skill sets which are scripting, system administration and networking and soft skill sets which are creative thinking and communication. Basically, one needs to constantly reinvent and learn upcoming technologies.
Technical Skills:
- In terms of essential cybersecurity skills, Networking tops the list. If one wants to aspire to become a penetration tester or network security engineer, that person needs to fully grasp underlying mechanisms various networking protocols and principles.
- Most network components and intrusion prevention systems run Linux as their operating system. Learning Linux helps to collect security data and perform security toughening.
- System administration is indispensable for cyber security specialists. Can user, for example, dictate what happens after downloading malware on windows operating system or extract files from a pc without knowing the log in credentials?
- To detect security loopholes in networks or security devices, it is necessary to have an outlook like a cybercriminal. White hat hackers try to safeguard data from both outside and inside threats by identifying vulnerabilities in systems that could be reduced. White hats are mainly utilized by the intended system’s owner and are handsomely compensated for their efforts. Their practice is not illegal since it is performed with the approval of the system owner.
- To become a cybersecurity practitioner, you wouldn’t need to be an extremely skilled programmer, but you must handle situations with an algorithmic mindset. Scripting is a wonderful way to learn the underlying working principles of hardware and software.
- Even though you wouldn’t want to become a programmer, it’s important to understand enough to read code.
- To run malware analysis, cybersecurity professionals ought to be accustomed with all virtual machine platforms.
Soft Skills
- Communication: You will need to invest a considerable amount of time training end users on how to set up their machines or implement security measures.
- New security hazards emerge all the time, so you must be able to continuously acquire new skills and techniques.
- On a regular basis, cybersecurity entails finding solutions to issues. If you really do not like to indulge in solving problems, a profession in cybersecurity is probably not just for you.
Top Cybersecurity Job roles: From beginner level to executive level
There are many high-paying, versatile full-time job vacancies in the industry. Due to the sheer world – wide scarcity of skilled talent pool, numerous recruiters are offering entry-level salaries ranging from Rs. ₹10L to ₹12L. Cybersecurity directors and chief information security officers (CISOs), for example, can obtain more than ₹90L per year.
- Cybersecurity Analyst: Security Operations Centre (SOC) analyst concentrates on the front-line attack detection. Cybersecurity analysts work in dedicated security hubs and must be competent in a variety of areas such as log analysis, Wireshark, malware analysis, and programming. A SOC analyst’s primary responsibility is to monitor network data. This particular job role has the potential to be used as a fantastic launchpad for next level of the roles.
- Penetration Tester: Penetration testers, also known as white hat hackers, are one of the most in-demand job positions in the cybersecurity industry. They are in charge of identifying and analyzing security flaws in organizational IT infrastructure along with that a penetration tester are asked to prepare a detailed report about their observations and procedures. Penetration testing is not a low-wage job rather it attracts one of the most handsome salaries in the industry.
- Cybersecurity Engineer: Cybersecurity engineers, like software engineers, create technologies that protect computer architecture. Their commitment is to foresee network security loopholes, which necessitates the installation of firewalls, the use of encryption software, and the revamping of patches. A few years of experience and a strong command in various scripting languages are required to become a cybersecurity engineer.

