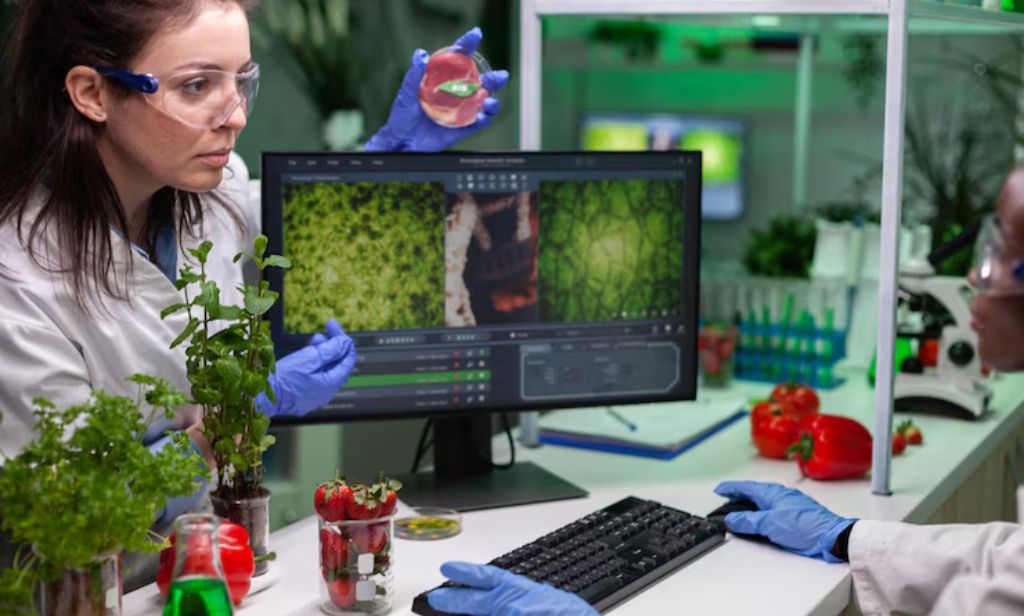

Today’s biotechnology industry is at the precursor of innovation, providing previously unheard-of chances to address urgent global issues. Exploring and using nature’s secrets and using the complex mechanisms of living things to create sustainable solutions, is at the heart of its goal (1). This essay explores the complex field of biotechnology and considers how it might help us understand nature’s
mysteries and move toward a more sustainable future is represented in fig 1.
Figure 1. Different aspects of sustainable Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a broad field of study that uses living things, biological systems, or their byproducts to create technologies and products with a range of uses. Fundamentally, biotechnology offers alternatives to traditional methods that frequently deplete finite resources and worsen the environment, holding up the promise of sustainability.
Bioprocess technology, which includes the design, optimization, and management of biological processes to generate useful products or services, is the foundation of biotechnology. Bioprocesses use the metabolic processes of cells, enzymes, and microbes to transform basic materials into desired products. This strategy has enormous promise for long-term fixes in a variety of fields, including environmental cleanup, healthcare, and agriculture. Through the use of microbial symbiosis, scientists have created biopesticides and biofertilizers that improve soil health and lessen the need for chemical inputs. Bioprocess technology provides environmentally friendly substitutes for conventional chemical synthesis techniques in the manufacturing sector. Biotechnologists use renewable feedstocks to create a broad range of bio-based chemicals, polymers, and medicines through fermentation and enzymatic catalysis. These bio-based goods pave the way for a greener industry by reducing dependency on fossil fuels and lessening the negative environmental effects of chemical manufacturing processes. Biological agents are used in bioremediation, one of the most exciting uses of bioprocess technology, to break down or sequester environmental toxins. Because of their extraordinary metabolic capacities, microorganisms are able to degrade a variety of pollutants, such as heavy metals, petroleum hydrocarbons, and persistent organic pollutants. Bioremediation is an economical and ecologically beneficial method of cleaning up contaminated locations and repairing ecosystems by utilizing the power of microbial communities.
Biotechnology has enormous potential, but in order to fulfill its promise of sustainability, a number of issues must be resolved. These include ethical and legal issues related to genetic engineering and bioprospecting, as well as technological obstacles including scalability, process optimization, and cost-effectiveness. However, biotechnology has the ability to transcend these obstacles and propel revolutionary change in the direction of a more sustainable future with sustained research, innovation, and cross-disciplinary cooperation. Unlocking nature’s secrets through biotechnology holds promise for addressing the complex challenges facing our planet. By utilizing the strength of biological systems responsibly, we can pave the way towards a more sustainable and resilient future for generations to come
Certainly! Here’s a simplified tabular format outlining some potential job prospects in biotechnology:
|
Job Title |
Description |
|
Biomedical Engineer |
Design and develop medical devices, equipment, and software used in healthcare settings. |
|
Biotechnologist |
Conduct research to develop new products, processes, and techniques in biotechnology. |
|
Biochemist |
Study the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. |
|
Genetic Counselor |
Provide guidance to individuals and families regarding genetic disorders and testing options. |
|
Pharmaceutical Scientist |
Develop and test new drugs and medications, ensuring safety and efficacy. |
|
Clinical Research Associate |
Coordinate and monitor clinical trials to evaluate the effectiveness of new medical treatments. |
|
Microbiologist |
Study microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, and their interactions with humans. |
|
Bioinformatics Specialist |
Analyze and interpret biological data using computational tools and techniques. |
|
Regulatory Affairs Manager |
Ensure compliance with government regulations and guidelines in the biotechnology industry. |
|
Quality Control Analyst |
Test and inspect biotechnological products to ensure they meet quality standards. |
This is just a snapshot of some potential job roles within the field of biotechnology. The field is diverse and continuously evolving, offering a wide range of career opportunities across various sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and environmental science.
Reference:
- Ulrich A.K. Betz, Loukik Arora, Reem A. et al. Game changers in science and technology – now and beyond, Technological Forecasting and Social Change, Volume 193, 2023, 122588, ISSN 0040-1625, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122588.
Visited 1075 times, 2 Visits today


