Any online transaction that consists of digital money is a piece of a challenge these days with the growing threats of hackers looking to steal bank info posted online. This leads to the invention of various kinds of crypto-currency money, Bitcoin is one of them. The generation behind the usage of Bitcoin is popularly referred to as BLOCKCHAIN.
Nowadays Blockchain has become a buzzword in both industry and academia. Blockchain is a constantly developing ledger that keeps a permanent document of all the transactions that have taken region in a relaxed, chronological, and immutable way. It is able to be used for the comfy transfer of cash, belongings, contracts, and so forth. Without requiring a 3rd- party intermediary such that a financial institution or government. Blockchain is a software protocol however it couldn’t be run without the net (like SMTP is for electronic mail).
It is a distributed database of information or in other words, it is a public ledger (files) of all transactions done in the online world. The Blockchain is innovation and a strategy that permits local area clients to approve, keep and synchronize the substance of an exchange record which is duplicated across numerous clients.
In the academic field, blockchain technology is also attracting more and more attention. The study of blockchain can be divided into three categories. Firstly, study on the digital currency that is based on blockchain, including the decentralized and centralized digital currency [4]. Secondly, study on the application of blockchain technology in non-digital currency scenarios such as the application of blockchain in smart cities [5] and medical information security management [6, 7]. Thirdly, study underlying blockchain technology. More and more researchers realize that the blockchain can be stripped out from digital currency to create a revolutionary technical architecture in other areas. Some researchers have begun to study the underlying technologies such as the difficult control of mining [8], the scalability of consensus algorithms [9] and the smart contract [10].
Career options in Blockchain
Blockchain technology can be used in diverse sets of applications. Blockchain technology can be implemented for finding solutions for different domains, such as healthcare, voting, identity management, governance, supply chain, energy resources and so on.
When the internet first came along, we had no idea how it would forever change our lives. From smartphones and text messages to streaming movies and video conferences with loved ones, as well as for attending meetings or interviews, no one knew the ways the world would change with the invention of the Internet. We are currently in the early phases of blockchain and there is much potential yet to be unlocked. The below figure represents some of the application domains of the blockchain proposed by various experts.
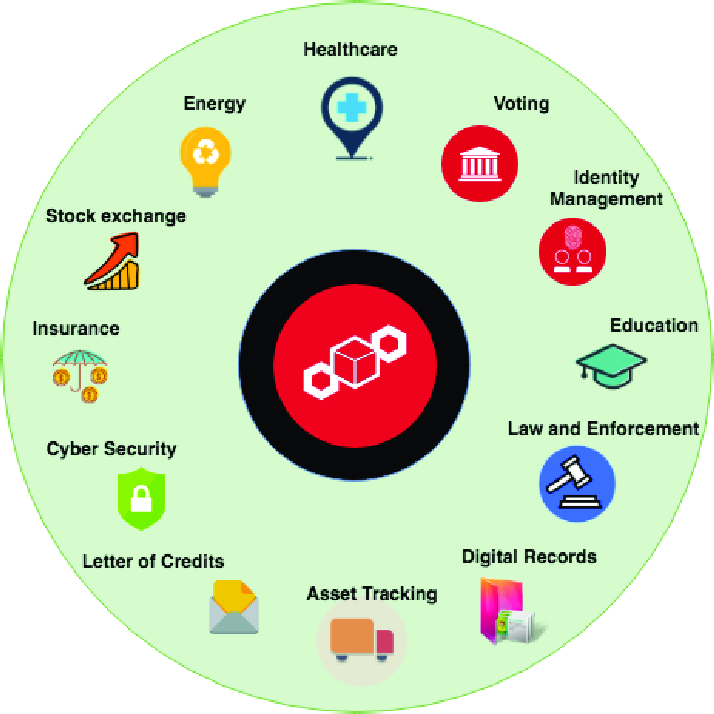
Healthcare: Blockchain technology can be used for the traceability of drugs and patient data management. Drug counterfeiting is a major problem in the pharmaceutical industry. Reports from the Health Research Funding organization revealed that 10% to 30% of the drugs sold in developing countries involves counterfeit [11]. It is estimated by the WHO that 16% of counterfeit drugs have the wrong ingredients, while 17% contain an imprecise level of essential ingredients. Therefore, these drugs can put a patient’s life in danger as they will not treat the diseases, rather can trigger secondary effects that can lead to death. Blockchain can be a solution to address this issue because all the transactions added to the distributed ledger are immutable and digitally time-stamped, which makes it possible to track a product and make the information tamper-proof. Managing patient data integrity is one of the major concerns for the healthcare industry. Each patient has unique physical variability. Therefore a treatment strategy for a common disease varies depending upon circumstances. Hence, for providing personalized treatment, it is necessary to access the complete medical history of an individual patient. However, medical data are sensitive and requires a secured sharing platform. The existing system of bookkeeping medical records is lacking privacy as well as interoperability. Currently, blockchain can offer an infrastructure for the integration of medical records among different healthcare facilities as well as data integrity features through its immutable ledger technology. Blockchain is capable of establishing a robust and secure transparent framework of storing digital medical records that brings quality services for the patients as well as reducing treatment costs.
Energy Industry: One of the main uses of blockchain in energy-related applications is in microgrids. A microgrid is a localized set of electric power sources and loads integrated and managed with the objective of enhancing energy production and consumption efficiencies and reliabilities [12]. The electric power sources can be distributed power generators, renewable energy stations, and energy storage components in facilities created and owned by different organizations or energy providers. One of the main
advantages of microgrid technology is that it does not only allow residents and other electric power consumers such as factories to have access to the needed energy, but they can also produce and sell excess energy to the grid. Blockchain can be used to facilitate, record, and validate power selling and buying transactions in microgrids.
Stock Market: Blockchain technology could solve the issues for fragmented market systems, such as interoperability, trust, and transparency [13]. Due to the role of intermediaries, the regulatory process and operational trade clearance, it takes more than 3 days to complete and finalize all transactions. As
a result, the stock market participants, for example, traders, regulators, brokers and the stock exchange are going through a cumbersome process. Blockchain may be the solution in this regard. It can make the stock exchange more optimal through decentralization and automation. By eliminating intermediaries and speeding up transaction settlements, blockchain can help reduce cost.
Voting: Blockchain can be utilized in different fields as a solution to the problems that a standard database might have. One such problem can be seen in voting. Recently, it was revealed that a major U.S. voting machine manufacturer had installed remote access software on some systems [14]. This software allowed for the alteration of votes when counting the total. Instances such as this create a lack of trust in America’s voting system, as seen in a recent poll:” Exclusive poll: Majority expects foreign meddling in midterms”. This poll suggests that only approximately a quarter of Americans feel confident that their vote is being counted. Blockchain would solve this issue by providing a distributed ledger that would ensure votes are counted since the ledger a voter owns is the same as the one counting the total.
Identity Management: In the real world, personal identity can be verified using identity documents such as a driver’s license, national ID card, and passport. However, there is hardly any effective equivalent system for securing online identities. Blockchain may render an approach to circumvent this concern. This technology can be used to create a platform to protect an individual’s identity from being theft or reduces fraudulent activities. Blockchain may allow individuals to create an encrypted identity that does not require any username or password while offering more security features and control over accessing their personal information. By comprising identity verification with that decentralized blockchain principle, a digital ID can be generated. This ID can be assigned to every online transaction similar to a watermark. Hence, it will aid organizations to detect and eliminate the possibility of fraud by checking identity on every real-time transaction Blockchain-based solutions on identity management could enable the consumer to access and verify online payments by simply using an app for authentication instead of using a username and password or biometric methods
Insurance: Blockchain can be used to support the insurance marketplace transactions between different clients, policyholders, and insurance companies. Blockchain can be used to negotiate, buy and register insurance policies, submit and process claims, and support reinsurance activities among insurance companies. Furthermore, blockchain enables insurance companies to be expanded globally.
References
- Danezis and S. Meiklejohn, “Centrally Banked Cryptocurrencies,” 2015.
- Biswas and V. Muthukkumarasamy, “Securing smart cities using blockchain technology,” in 18th IEEE International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, 14th IEEE International Conference on Smart City and 2nd IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Systems, HPCC/SmartCity/DSS 2016, December 12, 2016 – December 14, 2016, 2016, pp. 1392-1393.
- T. S. Liu, “Medical record system using blockchain, big data and tokenization,” in 18th International Conference on Information and Communications Security, ICICS 2016, November 29, 2016 – December 2, 2016, 2016, pp. 254-261
- Xiao, H. Wang, D. Jin, M. Li, and J. Wei, “Healthcare Data Gateways: Found Healthcare Intelligence on Blockchain with Novel Privacy Risk Control,” Journal of Medical Systems, vol. 40, p. 218, 2016.
- Kraft, “Difficulty control for blockchain-based consensus systems,”
Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, vol. 9, pp. 397-413, 2016-01-01 2016. - Vukoli, “The quest for scalable blockchain fabric: Proof-of-work vs.
BFT replication,” in IFIP WG 11.4 International Workshop on Open Problems in Network Security, iNetSec 2015, October 29, 2015 – October 29, 2015, 2016, pp. 112-125. - Idelberger, G. Governatori, R. Riveret, and G. Sartor, “Evaluation of
Logic-Based Smart Contracts for Blockchain Systems,”, Cham, Switzerland, 2016, pp. 167-83. - D. Glass, “Counterfeit drugs and medical devices in developing countries,” Research and Reports in Tropical Medicine, vol. 2014, pp. 11–22, 2014.
- H. Lasseter and P. Piagi, “Microgrid: A conceptual solution,” in IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, vol. 6. Citeseer, 2004, pp. 4285–4291.
- Lee, “New kids on the blockchain: How bitcoin’s technology could reinvent the stock market,” Hastings Bus. LJ, vol. 12, p. 81, 2015.
- D. Glass, “Counterfeit drugs and medical devices in developing countries,” Research and Reports in Tropical Medicine, vol. 2014, pp. 11–22, 2014.
- H. Lasseter and P. Piagi, “Microgrid: A conceptual solution,” in IEEE Power Electronics specialists Conference, vol. 6. Citeseer, 2004, pp. 4285–4291.
- Lee, “New kids on the blockchain: How bitcoin’s technology could
reinvent the stock market,” Hastings Bus. LJ, vol. 12, p. 81, 2015. - “Fair fight donate via ActBlue,” https://secure.actblue.com/donate/
fair-fight-reproductive-rights, (Accessed on 05/21/2019).
Visited 1404 times, 2 Visits today


